|
Beta vulgaris
French: betterave
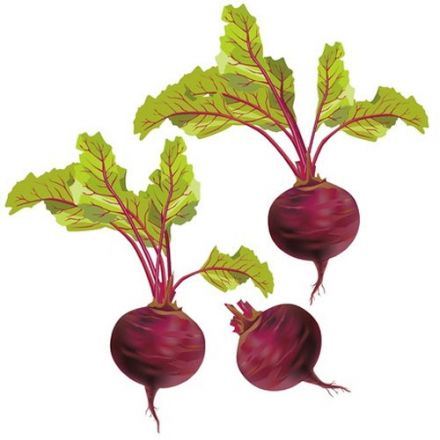
All about beet
Origin: the descendant of a wild species from the Mediterranean basin and Asia.
Etymology: from the Latin beta. A biennial plant of the Chenopodiaciae family, grown for its plump taproot.
Beets are commonly divided into three types: sugar beets, fodder beets (used as animal feed) and the red beets used for food. Long neglected, beets have become increasingly and successfully revived.
Round, flat or long, red or streaked with white or yellow, beets vary from one region to another. The beet is categorized with other root vegetables, including the carrot and turnip. The root can be round, flat or long, with its color ranging from red, red streaked with white, to yellow, etc.
Its red color comes from betacyanin, a pigment of the anthocyanin family.
Sugar Beet (B. vulgaris v. altissima)
How different things would be without the discovery in the 19th century of the sugar beet, responsible for half of all today’s refined sugar! The root, rich in sucrose, is used primarily for sugar production, and to a lesser extent for distilling. The sugar beet should not be confused with the common garden beet (Beta vulgaris var. conditiva). Did you know that the sugar beet’s diffusion was in large part due to Napoleon? He gave France the chance to replace sugar cane – which was no longer arriving in French ports because of the war with England and the continental blockade – by offering no less than 100,000 acres of land to whoever would undertake the cultivation of sugar beets, while also committing a million francs towards industrialists’ research.

-

 Recipes
Recipes
-

 Products
Products
-

 Entertaining
Entertaining
-

 Chefs
Chefs
-

 Hints & Tips
Hints & Tips
-
 Glossaries
Glossaries